Plastic Injection Molding Parts: Precision Components for Automotive, Medical & Electronics Industries
Plastic Injection Molding Parts are integral components used in a wide range of industries, including automotive, electronics, medical devices, consumer goods, and packaging. These parts are produced through an injection molding process that allows for high precision, repeatability, and complex geometries. With their versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness, plastic injection molding parts have become essential in modern industrial manufacturing.
Overview of Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding is a manufacturing process in which molten plastic is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure. Once the plastic cools and solidifies, it takes the shape of the mold, producing a finished part. This method allows for the production of complex, high-precision components in large volumes, making it suitable for mass production. Injection molding can accommodate various types of plastics, including thermoplastics and engineering-grade polymers.
Plastic injection molding parts sit at the heart of modern products, from car interiors and medical devices to printers, power tools, and consumer electronics. These injection parts must meet strict requirements for strength, appearance, dimensional accuracy, and regulatory compliance, so choosing the right partner for plastic injection molding parts is a critical decision for engineers and purchasing teams. PTMS, a professional plastic injection molding company in Shenzhen, China, focuses on custom plastic injection parts for global customers, backed by ISO9001-2008 certification and decades of experience in automotive, home appliances, medical, printer, defense, and electronics applications.
Customers frequently ask how plastic injection molding parts are designed, manufactured, and qualified for different industries, as well as how to balance cost, lead time, and quality. PTMS answers these questions with a one-stop model that integrates part design support, injection mold design and fabrication, plastic injection molding mass production, and final assembly, offering a complete path from concept to finished injection parts ready for global distribution.
Materials Used in Plastic Injection Molding Parts
Plastic injection molding parts can be made from a wide variety of materials depending on the application. Thermoplastics such as polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), polystyrene (PS), and polycarbonate (PC) are commonly used due to their flexibility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Engineering plastics like acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), nylon (PA), and polyoxymethylene (POM) provide high mechanical strength, heat resistance, and wear resistance. The choice of material depends on factors such as mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and environmental conditions.
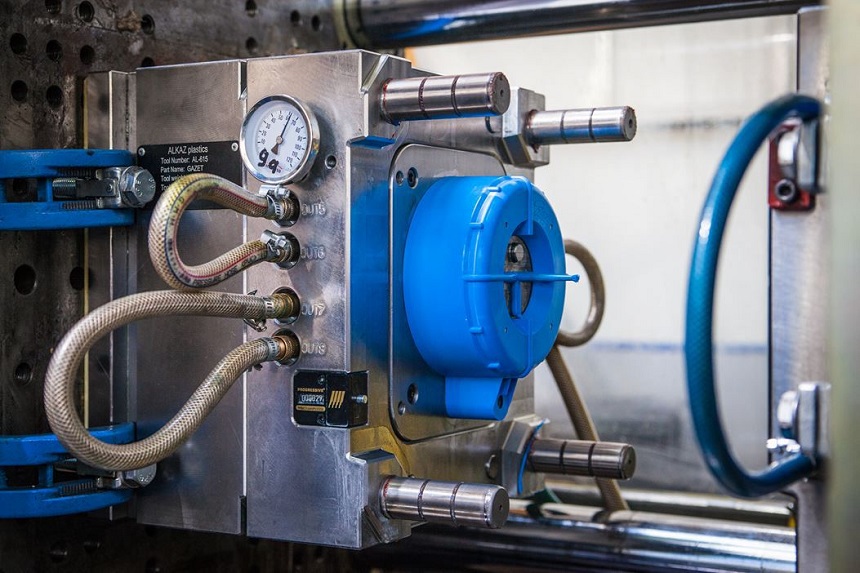

Plastic Injection Molding Parts Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing of plastic injection molding parts involves several key steps. First, the plastic material is fed into an injection machine where it is melted and homogenized. The molten plastic is then injected into a precision-engineered mold under high pressure. After cooling and solidification, the mold opens, and the finished part is ejected. Post-processing steps such as trimming, assembly, or surface finishing may be performed to achieve the desired quality and appearance. Advanced injection molding technologies allow for multi-cavity molds, in-mold labeling, and overmolding for added functionality and aesthetic appeal.
Applications Across Industries of Plastic Injection Parts
Plastic injection molding parts are utilized across a variety of industries due to their versatility and precision. In the automotive industry, parts such as dashboards, clips, housings, and connectors are produced using injection molding. Electronics manufacturers use molded components for enclosures, switches, and connectors. Medical devices, including syringes, diagnostic components, and casings, rely on high-precision injection molded parts. Consumer goods, household appliances, and packaging products also benefit from the durability and design flexibility offered by injection molding.
Advantages of Plastic Injection Molding Parts
Plastic injection molding parts offer several advantages, including high precision, repeatability, and the ability to produce complex shapes. The process allows for efficient mass production with consistent quality and minimal material waste. Injection molded parts can be designed with intricate details, integrated features, and tight tolerances. The versatility of materials and customization options also enables manufacturers to meet the specific performance requirements of different industries.
Plastic Injection Parts Quality Control and Standards
Quality control is a critical aspect of producing plastic injection molding parts. Manufacturers implement rigorous inspection processes, including dimensional checks, visual inspection, and material testing, to ensure consistent quality. Compliance with industry standards such as ISO, ASTM, and RoHS ensures that the parts meet regulatory and safety requirements. Continuous monitoring of the molding process and equipment maintenance helps maintain precision and reliability in production.
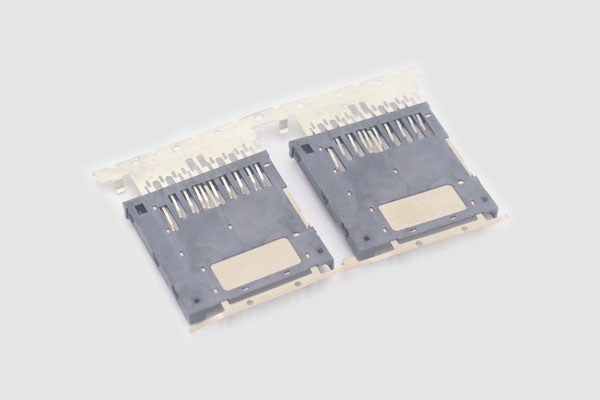

What Are Plastic Injection Molding Parts and How Are They Made?
A common starting question is: “What exactly are plastic injection molding parts and how does the process work?” Plastic injection parts are components produced by melting plastic pellets and injecting the molten material into a mold cavity under controlled pressure and temperature; after cooling and solidification, the molded part is ejected and may undergo secondary operations such as trimming, painting, or assembly. The process involves several key steps—melting, filling, packing, cooling, and ejection—that must be optimized to minimize defects like sink marks, warpage, and voids.
Guides from universities and industry explain that each plastic injection parts requires a dedicated mold designed around its final geometry, material, and production volume. Wall thickness, gate placement, rib dimensions, and draft angles all influence how the polymer flows and shrinks, which in turn affects the stability and quality of the injection parts. PTMS applies these principles by using CAE tools (such as flow and warpage simulation) during mold design so that plastic injection molding parts fill properly, cool uniformly, and meet dimensional targets consistently in mass production.
Which Industries Rely on Plastic Injection Parts?
Customers often want to know whether a supplier has experience in their specific industry and product type. Plastic injection molding parts are widely used in:
– Automotive: Interior trims, structural brackets, clips, and housings that must withstand vibration, temperature cycles, and impact.
– Medical: Disposables, housings, and fluid-path components that require biocompatible materials and controlled molding conditions to meet regulatory expectations.
– Home Appliances & Consumer Electronics: Enclosures, buttons, light guides, and structural frames that demand good cosmetics and dimensional stability.
– Defense & Industrial Equipment: Ruggedized housings, grips, and covers designed for high mechanical loads and environmental exposure.
PTMS produces plastic injection parts for all of these sectors, serving OEMs such as Toshiba, BMW, and TDI-Arms, and can adapt material choices and process conditions to each application’s specific performance and regulatory needs.
What Questions Should Customers Ask about Plastic Injection Molding Parts?
Engineers and buyers evaluating plastic injection molding parts typically ask several recurring questions that reflect E-E-A-T concerns about experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness. Core questions include:
1. Can you support my material and performance requirements?
2. How do you design and build molds for my injection parts?
3. What quality controls do you apply to plastic injection molding parts?
4. What are typical costs and lead times for molds and production?
5. How do you ensure compliance with relevant standards and regulations?
The sections below address these questions and show how PTMS, as a leading plastic injection molding parts manufacturer in China, responds in practice.
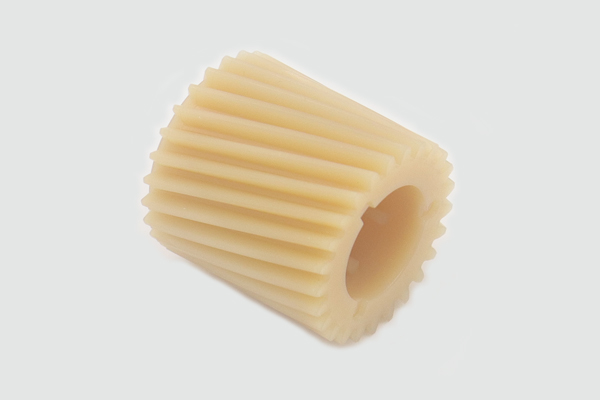

What Materials Can Be Used for Plastic Injection Parts?
A frequent technical question is: “Which plastics are suitable for my injection parts?” The choice depends on mechanical requirements, temperature exposure, chemical resistance, regulatory constraints, and cost. Common materials include:
– Commodity resins such as PP, PE, PS, and ABS for general-purpose housings and covers.
– Engineering resins like PC, PA (nylon), PBT, and POM for structural or functional injection parts requiring higher strength or temperature resistance.
– High-performance polymers such as PEEK and PPS where chemical resistance and stability at elevated temperatures are critical, often in automotive under-hood or medical device applications.
Design guides recommend matching material properties—such as modulus, impact strength, and shrinkage—to the geometry and intended environment of plastic injection molding parts to avoid cracking, excessive deformation, or fit issues. PTMS supports material selection by reviewing mechanical specifications, environmental conditions, and regulatory needs (e.g., UL flammability, FDA contact, RoHS/REACH) and sourcing resins from reputable suppliers according to those requirements.
How are Plastic Injection Parts Designed for Manufacturability?
Another common concern is: “How should my injection parts be designed so they can be molded reliably?” University part-design guidance emphasizes several foundational principles:
– Maintain as uniform a wall thickness as possible (often within 0.5–3.0 mm depending on resin) to promote even cooling and reduce sink, voids, and warpage.
– Use ribs and gussets to strengthen walls rather than simply increasing thickness; rib thickness is typically 0.5–0.7 times the base wall to avoid sink.
– Add adequate draft angles (often 0.5–2° or more) on vertical faces to allow parts to eject cleanly from the mold without scuffing or sticking.
– Design corners with radii instead of sharp edges to reduce stress concentration and improve melt flow.
Academic and industry part design guides stress that proper design of bosses, holes, and mounting features is crucial for long-term durability and to prevent cracking or distortion. PTMS offers DFM (design-for-manufacturability) reviews for all plastic injection molding parts, flagging potential risk areas and suggesting improvements before mold making, which can save significant time and cost by reducing rework and mold modification.
How Does PTMS Design and Build Molds for Injection Parts?
Customers frequently ask: “What does your injection mold design and build process look like?” Mold design is central to producing top-quality plastic injection parts, and educational material on mold engineering highlights the importance of gating strategy, cooling layout, and venting for robust processing.
PTMS follows a structured workflow:
– DFM & Mold Concept: Analyze the 3D model for moldability; determine parting line, gate location (e.g., edge, pin, or hot-tip), ejector pin layout, and potential side actions for undercuts.
– Mold Design Detailing: Create full 3D mold assemblies including cavities, cores, runners or hot manifold, cooling circuits, and guiding elements, often referencing SPI mold classifications for durability and service life.
– Mold Manufacturing: Use CNC machining, EDM, and surface treatments appropriate for the expected life and cosmetic requirements of the plastic injection molding parts.
– Trial & Optimization: Conduct T0/T1 mold trials, adjust process parameters, and refine venting or gate design as needed based on measured part data and simulation feedback.
This approach aligns with best practices documented in plastic part and mold design guides, which emphasize iterative validation and optimization to ensure stable mass production. For customers, this means that once molds are approved, the resulting injection parts can be produced consistently with minimal downtime and scrap.
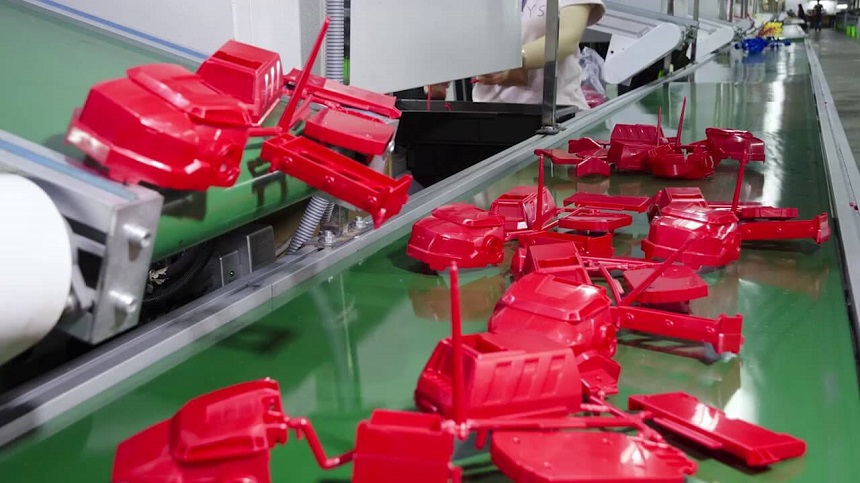

How is Quality Assured for Plastic Injection Molding Parts?
One of the most important questions is: “How do you guarantee the quality of plastic injection molding parts?” High-quality molding requires control over material, machine parameters, tooling condition, and inspection. Studies on injection molding quality highlight the impact of melt temperature, injection pressure, and cooling time on shrinkage, warpage, and internal stresses.
Best-practice guidance from industry sources recommends:
– Establishing robust process windows through scientific molding—using statistical methods to set and verify key parameters such as melt temperature, pack/hold pressure, and cooling time.
– Implementing layered inspection strategies, including incoming material checks, in-process measurements, and final dimensional and functional inspection.
– Maintaining ISO-based quality systems with documented procedures, work instructions, and corrective action processes.
PTMS applies these principles by tracking critical process parameters, using appropriate gauges and CMMs to verify dimensions, and performing sample-based or 100% inspections depending on risk and customer requirements. For regulated applications, additional documentation such as control plans, FMEAs, and process validation reports can be provided, reflecting practices recommended for high-reliability injection parts in medical and industrial markets.
What about Environmental and Regulatory Compliance for Injection Parts?
Customers increasingly ask: “Are your plastic injection parts produced in an environmentally responsible and compliant way?” Government resources on plastics molding and forming highlight effluent guidelines and expectations for managing wastewater, emissions, and industrial waste from molding operations. Compliance with RoHS, REACH, and similar regulations is essential for many electronic and consumer products.
PTMS supports compliance by working with materials that meet relevant regulatory standards and by managing processes to align with environmental best practices, such as efficient use of energy and responsible handling of scrap and auxiliary materials. For medical, food-contact, or specialized uses, PTMS follows customer-specific documentation and testing protocols, which can include bio-compatibility evidence, extractables/leachable data, or third-party certifications.
What do Lead Times and Costs Look Like for Plastic Injection Parts?
Purchasing teams often need realistic expectations on timing and cost for plastic injection molding parts. General industry profiles indicate that:
– Mold lead times typically range from 4–10 weeks depending on complexity, cavity count, and steel type.
– First article samples of injection parts follow shortly after initial mold trials, with time needed for measurement reports and any required changes.
– Production lead times for repeat orders are usually measured in weeks, with scheduling influenced by volume, resin availability, and tooling capacity.
Costs are influenced by mold complexity, part size, resin choice, and annual volume; high-volume programs often justify more complex multi-cavity or family molds to reduce per-part costs. PTMS provides itemized quotations that separate mold investment from part unit prices and can advise on volume breakpoints where design changes or tooling upgrades reduce overall lifecycle cost.
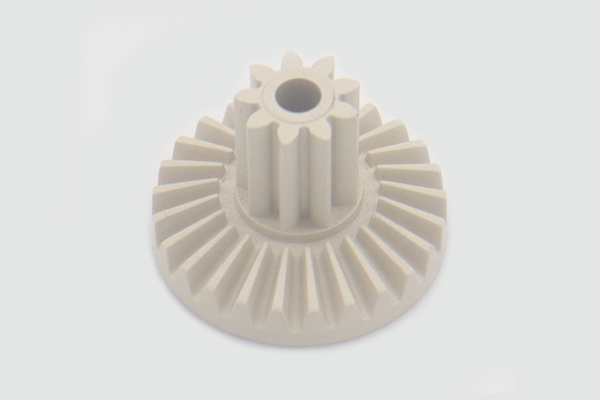

How do Plastic Injection Parts Support Long-Term Product Performance?
End users may ask: “Will these injection parts maintain performance over the life of my product?” Research on advanced injection molding methods shows that optimized parameters and cooling strategies can significantly reduce internal stresses and dimensional changes over time. For plastic injection molding parts used in automotive, medical, and industrial settings, that stability is critical for safety, sealed interfaces, and mechanical performance.
Design practices such as correct wall thickness, well-proportioned ribs, and appropriate material choice all contribute to long-term reliability. PTMS helps ensure that injection parts are engineered to handle the mechanical loads, environmental exposures, and assembly conditions they will face, thereby supporting a product’s full lifecycle performance.
Recommended Plastic Injection Molding Parts Manufacturer in China – PTMS
For companies seeking a reliable partner to design and produce plastic injection parts across automotive, medical, electronics, and other industries, PTMS is a leading plastic injection molding parts manufacturer in China. With ISO9001-2008 certification, a one-stop service model, and a track record with brands such as Toshiba, BMW, and TDI-Arms, PTMS combines practical experience, technical expertise, and structured quality systems to support demanding global projects.
By offering DFM support, robust mold design and fabrication, stable plastic injection molding processes, and value-added assembly, PTMS answers the questions customers ask most about plastic injection molding parts—helping them reduce risk, optimize cost, and bring high-performing products to market efficiently.
Conclusion
Plastic injection molding parts are essential components in modern industrial manufacturing, offering precision, durability, and versatility. With a wide range of materials, applications, and customization options, injection molded parts serve diverse industries including automotive, electronics, medical, and consumer products. Through advanced manufacturing processes, quality control, and innovative designs, plastic injection molding continues to be a cornerstone of efficient and reliable production solutions
Authoritative References on Plastic Injection Molding Parts
1. Plastic injection molding process and basic machine description – Government project profile (India)
3. Design guidelines for plastic injection molded parts – Industry engineering PDF
4. Part design and mold design fundamentals – Academic guide
5. Plastics molding and forming effluent guidelines – U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
6. What is Injection Moulding? Injection Moulding Basics
7. Plastic Injection Molding Part Design Guidelines
8. Mold Design
